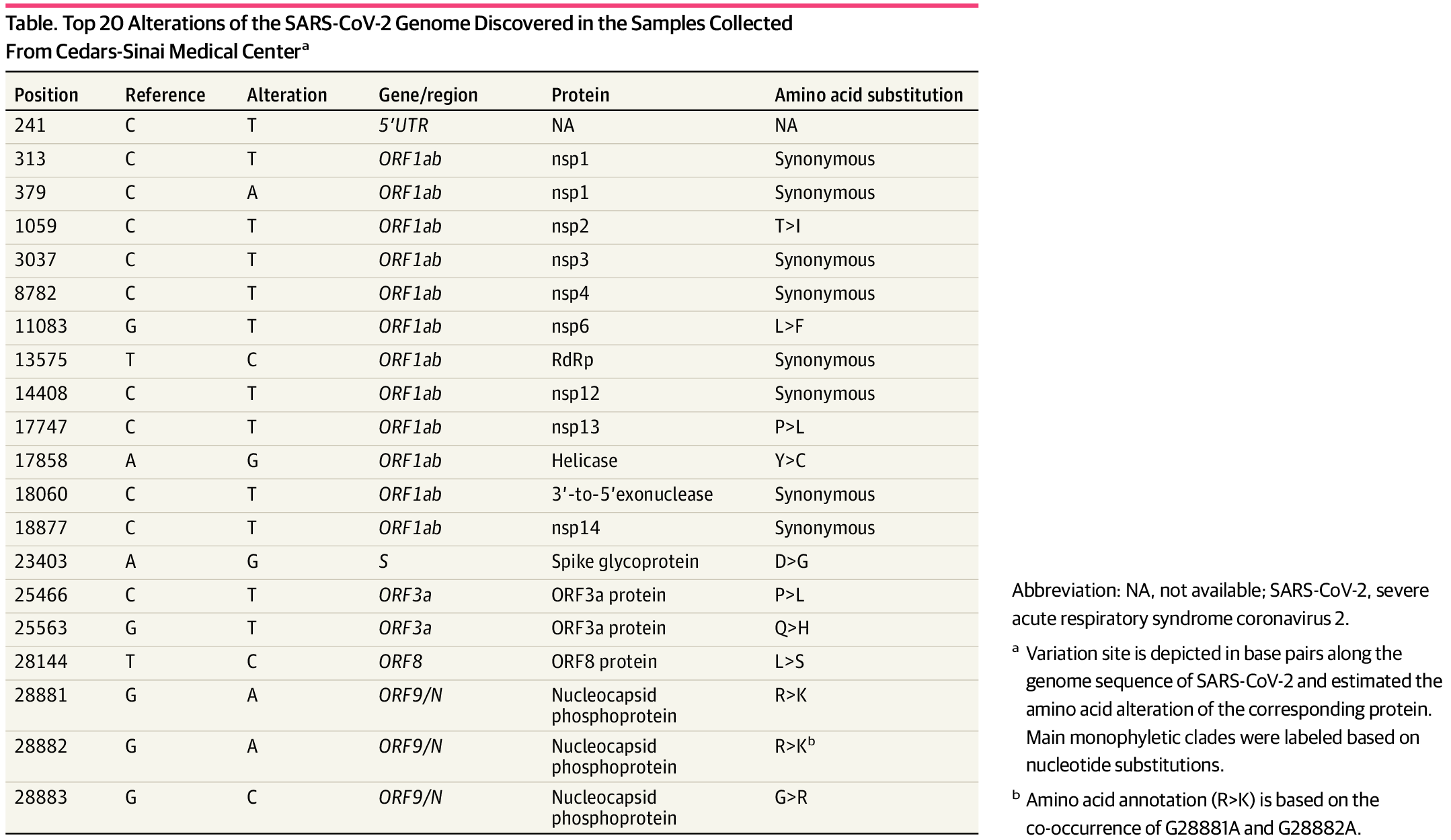
A patchwork approach to contact tracing across state health departments is making it increasingly difficult to know where people are getting exposed to COVID-19.
While some states like Louisiana and Washington state publicly track detailed data related to COVID-19 cases in bars, camps, daycares, churches, worksites and restaurants, most states do not, creating obstacles to preventing future cases.
The extensive spread of the virus, combined with the country's 50-state approach to pandemic response, has led to a dearth of information about where transmissions are occurring. Those shortcomings are in turn complicating efforts to safely open the economy and to understand the risks associated with certain activities and settings.








Recent Comments